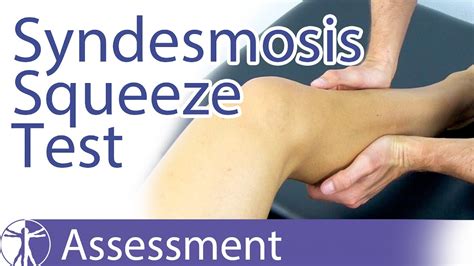
distal tibiofibular compression test|The distal tibiofibular compression test. : bespoke Objective To investigate the clinical effect of internal fixation of a Ni–Ti arched shape-memory connector in the treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis ligament injury.
Portal de notícias de Cascavel e Região. Após forte batida, c.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBSalve aí, rapaziada! De boa?O celular da Hannah enfim foi desbloqueado e com isso seus segredos também! O que iremos descobrir?Simbora conferir essa aventura.
The purpose of the squeeze test is to aid in the diagnosis of syndesmotic ankle sprains. The squeeze test is also known as the fibular compression test and available literature . See moreThe squeeze test compresses the proximal fibula against the tibia to assess the integrity of the bones, interosseus membrane, and . See moreThe squeeze test has been found to have moderate reliability (kappa = 0.50) according to a study performed by Alonso et al. and according to the study done by de César PC et al, the test has a sensitivity of 30% and a specificity of 93.5% for a high . See more High Ankle Sprain & Syndesmosis Injuries are traumatic injuries that affect the distal tibiofibular ligaments and most commonly occur due to sudden external rotation of the ankle. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with .
Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures (syndesmosis)
Objective To investigate the clinical effect of internal fixation of a Ni–Ti arched shape-memory connector in the treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis ligament injury.Tibia, fibula, syndesmosis, and the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. Positive Test. Pain above or below the sight of the squeeze is indicative of a fracture of the tibia or fibula, or sprain of the .
A positive test is noted when pain in the area of the distal tibiofibular joint is felt. Cotton test [ 33 ], the talus is ‘rocked’ from side to side in the ankle mortise by applying .The “squeeze test” is a clinical test for detecting “stable” syndesmosis injuries. The test is positive when proximal compression of the calf produces pain in the area of the distal tibiofibular and .
The distal tibiofibular compression test.
The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test (also known as the fibular compression test or Distal Tibiofibular Compression) is used for evaluation of an injury to the tibiofibular syndesmosis. The pressure is applied transversely .Next, a complete diagnostic arthroscopic examination is done to include evaluating for distal tibiofibular stability, osteochondral defects, and deep deltoid continuity. Arthroscopic stability .At this meeting, the investi- gator provided an overview of the study, a description of the function of the distal tibiofibular joint, and a review of the four orthopaedic tests proposed as .
When positive, proximal compression produces distal pain around the distal tibiofibular joint. External rotation stress test as described by Boytim , external rotation force is tenderness over the AITFL, swellingapplied to the ankle in a plantigrade position with the knee flexed 90°. A positive test is noted when pain in the area of the distal .
2. Squeeze test 3. Dorsiflexion compression test 4. Heel thump test 1. External rotation test is a test to identify a tibiofibular syndesmosis. The clinician has to maintain the ankle in dorsiflexion with an external rotation during a stabilized leg on the affected limb. The test can be implemented while the patient is sitting or lying down.
In a biomechanical study assessing the effects of varying tension on a suture button construct in fixation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis using static loads in a custom frame, the authors found that 8 to 12 kg of .Next, mobility of the distal tibiofibular joint (Figure 3) . Noble compression test also did not reproduce pain with passive flexion and extension of the knee. Although these special tests are commonly performed in the assessment of lower extremity dysfunction, the sensitivity and specificity for iliotibial band syndrome has not been . Background Non-invasive diagnosis of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis instability (DTSI) was a great challenge to clinicians. We designed a new method, the Standing on single foot-Binding test, and investigated the accuracy of the test in the diagnosis of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis instability in adults with a history of ankle injury. Methods 85 participants with . (A) External rotation test. (B) Dorsiflexion compression test: ankle is in maximal dorsiflexion with the patient weight bearing and force is applied over both malleoli. If syndesmotic injury is present then pain may be elicited over distal fibula. The test above can be useful in sprains where a patient can tolerate examination.
Disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis is frequently accompanied by rotational ankle fracture such as pronation-external rotation and rarely occurs without ankle fracture. . The squeeze test was considered positive when compression of the fibula to the tibia above the midpoint of the calf produced distal pain in the area of the .The “squeeze test” is a clinical test for detecting “stable” syndesmosis injuries. The test is positive when proximal compression of the calf produces pain in the area of the distal tibiofibular and interosseous ligaments. Background Tibiofibular syndesmosis injury leads to ankle pain and dysfunction when ankle injuries are not treated properly. Despite several studies having been performed, many questions about diagnosis and treatment remain unanswered, especially in ankle syndesmosis injury with interosseous membrane injury. Therefore, the purpose of this study .The "squeeze test" is a clinical test for detecting "stable" syndesmosis injuries. The test is positive when proximal compression of the calf produces pain in the area of the distal tibiofibular and interosseous ligaments. The purpose of this study was to examine what fibular movement, if any, occur .
A positive test results in an increased range of motion or less pain . It is a highly sensitive test (75%) . Squeeze test: consists of compression of the tibia and fibula in the middle leg to reproduce distal tibiofibular pain during diastasis and instability (Fig. 3). It has 30% sensitivity and 88–93.5% specificity.Injury to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis (DTFS) may be more common than previously reported. . Special tests which enhance the recognition of DTFS injury, such as the external rotation stress test and the distal tibiofibular compression test, and a rehabilitation progression are presented. Publication types In cadaveric studies, significant displacement at the anterior syndesmosis of roughly 0.2 to 0.3 mm is produced with the squeeze test only after the anterior tibiofibular, posterior tibiofibular, and anterior deltoid ligaments were all sectioned. 36, 64 The test appears to stress the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament the most as complete . A careful evaluation of the distal tibiofibular relationship with regard to the medial clear space, the tibiofibular clear space, and the tibiofibular overlap is crucial (16, 17 and 18). A radiograph of the uninjured ankle can be utilized to help clarify the normal anatomic relationship of distal tibia and fibula . We use weight-bearing .
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright .
The squeeze test involves mid-calf compression of the tibia and fibula which is thought to cause separation at the distal tibiofibular joint, in turn increasing tension in the remaining syndesmosis ligament fibres resulting in pain at the .
palpation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, pain during the squeeze test (manual compression of the tibia and fibula in the middle third of the leg), pain during the external rotation test and an inability to stand on the tip of the affected foot. Exclusion criteria Bilateral ankle sprain. Previous ankle surgery.Effect of Distal Tibiofibular Destabilization and Syndesmosis Compression on the Flexibility Kinematics of the Ankle Bones: An In Vitro Human Cadaveric Model . tibiofibular syndesmosis, compression, anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, interosseous membrane, . A Mauchly test of sphericity was used to assess the assumption of sphericity .The squeeze test, which involves approximating the tibia and fibula together in the proximal 1/3rd of the calf, has a positive predictive value of 6% and an inter-examiner reliability of .50. 3, 14 The external rotation stress test, whereby the foot is externally rotated while the leg, with knee flexed to 90, remains stable has a positive .
distal tibiofibular syn- desmosis have been argued to be more common than previously suspected by a number of researchers (2,4,12- 14,17,19). In their recent overview of . and doniflexion-compression test. Kappa coefiicient testing indicated that the external rotation test had the best interrater reliability (K = 0.751. The squeeze test was MRI, on the other hand, is the examination of choice for syndesmosis lesion diagnosis, with good sensitivity and specificity. Examination modalities, however, including slice orientation and ankle positioning in particular, need standardizing so as to enable good distal tibiofibular ligament visualization [58], [59].
The Cotton test is a stress test performed by pulling the fibula laterally to identify the widening of the tibiofibular clear space. This stress test will be positive if the tibiofibular clear space is wider than 1–2 mm as compared to the non-stress condition and it should be more than 5 mm when evaluated by fluoroscopy. 109,110 The External . A syndesmosis is a fibrous joint characterized by two adjacent bones connected by ligamentous structures, including a strong interosseous membrane (IOM). [1] The distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, which is comprised of two bones, the distal tibia and distal fibula, and four stabilizing ligaments, the anterior-inferior and posterior-inferior tibiofibular ligaments . The superior tibiofibular joint is innervated by the common fibular nerve (recurrent branch) and the nerve to popliteus muscle.. The former is a branch of the sciatic nerve, while the latter stems from the tibial nerve.. Blood supply. Blood supply to the superior tibiofibular joint comes from two branches of the anterior tibial artery; anterior and posterior tibial recurrent . similar effectiveness to manual ER stress test. Cotton/hook test. . compression plates. . (trans-syndesmotic fracture-dislocations in which the talus is driven into the distal tibiofibular articulation) neurologic injury . superficial peroneal nerve injury (10-15%)
A musculoskeletal simulator at ±7.5 Nm was used to test flexibility in dorsiflexion-plantarflexion, inversion-eversion, and internal-external rotation. After intact testing, syndesmotic probes were used to arthroscopically measure the intact position of .2. A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific than the test done withing the 24-48 hours. 3. A sensitivity of 52% has been reported in a single study for the inversion talar tilt test. 4. In acute injuries, the eversion stress test may be of limited clinical value.
drop test materials
drop test meaning in hindi
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
distal tibiofibular compression test|The distal tibiofibular compression test.